
Finally, the -j parameter stands for jump.The -s parameter, along with the IP address (198.51.100.0), indicates the source.To indicate a specific placement in the chain, you may also use a number with the -I option. Using a rule with the insertion option will add it to the beginning of a chain and will be applied first. Basic iptables Parameters and Syntaxīefore we begin creating rules, let’s review the syntax of an iptables rule.įor example, the following command adds a rule to the beginning of the chain that will drop all packets from the address 198.51.100.0: iptables -I INPUT -s 198.51.100.0 -j DROP The table contains a variety of built-in chains, but you can add your own. You can define different tables to handle these rules through chains, lists of rules that match a subset of packets. As stated above, iptables sets the rules that control network traffic. Many options can be used with the iptables command.
Use Linux iptables to Manage IPv4 Traffic The iptables Command

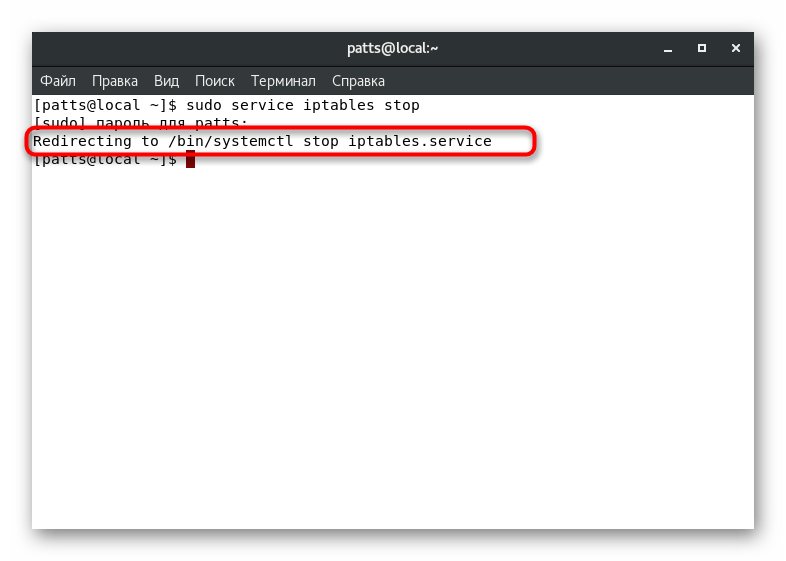
In order to use iptables, you will need root ( sudo) privileges.

By default, the iptables tool is included with your Linode-supplied distribution.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
